| Identification | More | [Name]
CYCLOHEXYL ISOCYANIDE | [CAS]
931-53-3 | [Synonyms]
BIO-FARMA BF001328
CYCLOHEXYL ISOCYANIDE
CYCLOHEXYL ISONITRILE
HANSA ISN-0519
ISOCYANOCYCLOHEXANE
Cyclohexane, isocyano-
Cyclohexaneisonitrile
Cyclohexyl #niso-cyanide
Cyclohexane, isocyano-(9CI) | [EINECS(EC#)]
213-238-7 | [Molecular Formula]
C7H11N | [MDL Number]
MFCD00003839 | [Molecular Weight]
109.17 | [MOL File]
931-53-3.mol |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Appearance]
colourless liquid | [Melting point ]
6.45°C | [Boiling point ]
173-176 °C
| [density ]
0.878 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
| [refractive index ]
n20/D 1.45(lit.)
| [Fp ]
170 °F
| [storage temp. ]
2-8°C
| [form ]
Liquid | [color ]
Clear colorless to slightly brown | [Stability:]
Stable. Incompatible with strong acids, strong bases, strong reducing agents, strong oxidizing agents. Flammable. | [BRN ]
3662332 | [CAS DataBase Reference]
931-53-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| Questions And Answer(Q&A) | Back Directory | [Preparation]
CAUTION: Use a well-ventilated hood and take all precautions before using phosgene.
To a flask equipped as in Preparation 3-1 is added 1.27 kg (10.0 moles) of N-cyclohexylformamide, 3.20 liters of triethylamine, and 4.50 liters of methylene chloride. The solution is stirred while phosgene is rapidly added (300-400 gm/hr) to cause vigorous refluxing. Refluxing ceases after 1.04 kg (10.2 moles) of phosgene have been added and the addition is stopped. The reaction mixture is cooled to 22-25°C, 400 gm (23.5 moles) of ammonia gas added over a period of 1-2 hr, the mixture filtered then concentrated under reduced pressure, and the residue distilled to afford 955 gm (88%), b.p. 67-72°C (14 mm Hg).
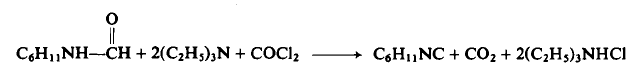
|
| Safety Data | Back Directory | [Hazard Codes ]
Xn | [Risk Statements ]
R20/21/22:Harmful by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed . | [Safety Statements ]
S36/37:Wear suitable protective clothing and gloves . | [RIDADR ]
UN 2810 6.1/PG 2
| [WGK Germany ]
3
| [F ]
10-13-21 | [HazardClass ]
6.1 | [PackingGroup ]
III | [HS Code ]
29299090 |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Chemical Properties]
colourless liquid | [Uses]
Cyclohexyl Isocyanide can be used as novel arginase inhibitors to treat diseases. | [Definition]
ChEBI: Cyclohexyl isocyanide is an isocyanide having a cyclohexyl group attached to nitrogen. It is a conjugate base of a cyclohexyl isocyanide(1+). | [General Description]
Cyclohexyl isocyanide reacts with dimethyl acetylenedicarboxylate to give a mixture of cyclopenta[b]pyridine derivatives, azaspirononatriene derivative and the azabicyclononatriene. It reacts with dialkyl acetylenedicarboxylates to form 1:1 intermediate which on facile addition to 1-benzylisatin and tryptantrin yields highly functionalized novel unsaturated γ-spiroiminolactones. | [References]
[1] Khalili, Gholamhossein. “ChemInform Abstract: A Diastereoselective Synthesis of (Z)-3-[(Aryl)(hydroxyimino)methyl] -2-cyclohexyl-1-(cyclohexylamino)imidazo[5,1-a]isoquinolinium Chlorides from Isoquinoline, Chlorooximes, and Cyclohexyl Isocyanide.” ChemInform 47 25 (2016).
[2] M. Anary‐Abbasinejad, M. Heidari, N. Shams. “One-pot synthesis of highly functionalised 1H-pyrazoles from arylcarbohydrazides, cyclohexyl isocyanide, and acetylene diesters.” Arkivoc 2012 1 (2012).
[3] Anary‐Abbasinejad, M. M. Jaafari and Mahdiyeh Talebizadeh. “One-pot Four-component Reaction between Arylamines, Arylglyoxals, Cyclohexyl Isocyanide, and Acetylene Diesters: An Efficient Synthesis of 2H-iminopyran Derivatives.” 2019. 0.
[4] Alireza Hassanabadi. “ChemInform Abstract: Use of Cyclohexyl Isocyanide in the Esterification of N-Benzoyl α-Amino Acid Derivatives.” ChemInform 43 3 (2011).
[5] A. Hassanabadi. “The use of cyclohexyl isocyanide in the esterification of N -benzoyl α-amino acids derivatives.” Journal of Chemical Research-s 18 1 (2011): 468–470.
|
|
|