

*Storage: {[sel_prStorage]}
*Shipping: {[sel_prShipping]}
Isatin is an endogenous monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitor that preferentially inhibits MAO-B activity with an IC50 of 3 μM. It also binds to other receptors and has broad physiological effects.
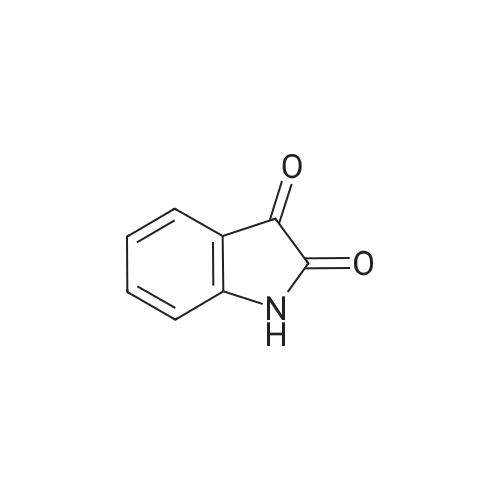
Synonyms: Indoline-2,3-dione
4.5




 *For research use only!
*For research use only!
Change View
| Size | Price | VIP Price | USA Stock *0-1 Day |
Global Stock *5-7 Days |
In Stock | ||
| {[ item.pr_size ]} |
Inquiry
{[ getRatePrice(item.pr_usd, 1,1,item.pr_is_large_size_no_price, item.pr_usd) ]} {[ getRatePrice(item.pr_usd,item.pr_rate,1,item.pr_is_large_size_no_price, item.discount_usd) ]} {[ getRatePrice(item.pr_usd, 1,1,item.pr_is_large_size_no_price, item.pr_usd) ]} |
Inquiry {[ getRatePrice(item.pr_usd,item.pr_rate,item.mem_rate,item.pr_is_large_size_no_price, item.vip_usd) ]} | Inquiry {[ item.pr_usastock ]} In Stock Inquiry - | {[ item.pr_chinastock ]} {[ item.pr_remark ]} In Stock 1-2 weeks - Inquiry - | Login | - + | Inquiry |
Please Login or Create an Account to: See VIP prices and availability
1-2weeks
Inquiry
{[ getRatePrice(item.pr_usd,item.pr_rate,item.mem_rate,item.pr_is_large_size_no_price, item.vip_usd) ]}
{[ getRatePrice(item.pr_usd, 1,1,item.pr_is_large_size_no_price, item.pr_usd) ]}
{[ getRatePrice(item.pr_usd,1,item.mem_rate,item.pr_is_large_size_no_price, item.pr_usd) ]}
Inquiry
{[ getRatePrice(item.pr_usd,item.pr_rate,1,item.pr_is_large_size_no_price, item.vip_usd) ]}
{[ getRatePrice(item.pr_usd, 1,1,item.pr_is_large_size_no_price, item.pr_usd) ]}
{[ getRatePrice(item.pr_usd, 1,1,item.pr_is_large_size_no_price, item.pr_usd) ]}
In Stock
- +
Please Login or Create an Account to: See VIP prices and availability
Search for reports by entering the product batch number.
Batch number can be found on the product's label following the word 'Batch'.
Search for reports by entering the product batch number.
Batch number can be found on the product's label following the word 'Batch'.
Search for reports by entering the product batch number.
Batch number can be found on the product's label following the word 'Batch'.
Search for reports by entering the product batch number.
Batch number can be found on the product's label following the word 'Batch'.
Search for reports by entering the product batch number.
Batch number can be found on the product's label following the word 'Batch'.
Hwang, Dong-Jin ; He, Yali ; Ponnusamy, Suriyan , et al. J. Med. Chem.,2023,66(5):3372-3392.
Abstract: A major challenge for new drug discovery in the area of androgen receptor (AR) antagonists lies in predicting the druggable properties that will enable small mols. to retain their potency and stability during further studies in vitro and in vivo. Indole (compound 8) is a first-in-class AR antagonist with very high potency (IC50 = 0.085 μM) but is metabolically unstable. During the metabolic studies described herein, we synthesized new small mols. that exhibit significantly improved stability while retaining potent antagonistic activity for an AR. This structure-activity relationship (SAR) study of more than 50 compounds classified with three classes (Class I, II, and III) and discovered two compounds (32c and 35i) that are potent AR antagonists (e.g., IC50 = 0.021 μM, T1/2 = 120 min for compound 35i). The new antagonists exhibited improved in vivo pharmacokinetics (PK) with high efficacy antiandrogen activity in Hershberger and antiandrogen Enz-Res tumor xenograft models that overexpress AR (LNCaP-AR).
Show More >

The evaluation of isatin analogues as inhibitors of monoamine oxidase
Prinsloo, Izak F. ; Petzer, Jacobus P. ; Cloete, Theunis T. , et al. Chem. Biol. Drug Des.,2023,102(5):1067-1074.
Abstract: The small mol., isatin, is a well-known reversible inhibitor of the monoamine oxidase (MAO) enzymes with IC50 values of 12.3 and 4.86μM for MAO-A and MAO-B, resp. While the interaction of isatin with MAO-B has been characterized, only a few studies have explored structure-activity relationships (SARs) of MAO inhibition by isatin analogs. The current study therefore evaluated a series of 14 isatin analogs as in vitro inhibitors of human MAO-A and MAO-B. The results indicated good potency MAO inhibition for some isatin analogs with five compounds exhibiting IC50 < 1μM. 4-Chloroisatin (1b) and 5-bromoisatin (1f) were the most potent inhibitors with IC50 values of 0.812 and 0.125μM for MAO-A and MAO-B, resp. These compounds were also found to be competitive inhibitors of MAO-A and MAO-B with Ki values of 0.311 and 0.033μM, resp. Among the SARs, it was interesting to note that C5-substitution was particularly beneficial for MAO-B inhibition. MAO inhibitors are established drugs for the treatment of neuropsychiatric and neurodegenerative disorders, while potential new roles in prostate cancer and cardiovascular disease are being investigated.
Show More >
Keywords: competitive ; inhibition ; isatin ; monoamine oxidase ; structure-activity relationship
Show More >
Purchased from AmBeed: 6341-92-0 ; 91-56-5 ; 1127-59-9 ; 611-09-6 ; 7477-63-6 ; 6344-05-4 ; 443-69-6 ; 87-48-9 ; 39603-24-2 ; 608-05-9 ; 17630-76-1 ; 20205-43-0 ; 131609-60-4 ; 150560-58-0 ; 57816-97-4
Show More >

| CAS No. : | 91-56-5 |
| Formula : | C8H5NO2 |
| Linear Structure Formula : | C6H4NH(CO)2 |
| M.W : | 147.13 |
| Synonyms : |
Indoline-2,3-dione
|
| MDL No. : | MFCD00005718 |
| InChI Key : | JXDYKVIHCLTXOP-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Pubchem ID : | 7054 |
| GHS Pictogram: |

|
| Signal Word: | Warning |
| Hazard Statements: | H302-H315-H319-H332-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements: | P261-P280-P305+P351+P338 |
| Num. heavy atoms | 11 |
| Num. arom. heavy atoms | 6 |
| Fraction Csp3 | 0.0 |
| Num. rotatable bonds | 0 |
| Num. H-bond acceptors | 2.0 |
| Num. H-bond donors | 1.0 |
| Molar Refractivity | 42.16 |
| TPSA ? Topological Polar Surface Area: Calculated from |
46.17 ?2 |
| Log Po/w (iLOGP)? iLOGP: in-house physics-based method implemented from |
0.83 |
| Log Po/w (XLOGP3)? XLOGP3: Atomistic and knowledge-based method calculated by |
0.83 |
| Log Po/w (WLOGP)? WLOGP: Atomistic method implemented from |
0.25 |
| Log Po/w (MLOGP)? MLOGP: Topological method implemented from |
0.17 |
| Log Po/w (SILICOS-IT)? SILICOS-IT: Hybrid fragmental/topological method calculated by |
1.55 |
| Consensus Log Po/w? Consensus Log Po/w: Average of all five predictions |
0.72 |
| Log S (ESOL):? ESOL: Topological method implemented from |
-1.68 |
| Solubility | 3.08 mg/ml ; 0.021 mol/l |
| Class? Solubility class: Log S scale |
Very soluble |
| Log S (Ali)? Ali: Topological method implemented from |
-1.38 |
| Solubility | 6.1 mg/ml ; 0.0415 mol/l |
| Class? Solubility class: Log S scale |
Very soluble |
| Log S (SILICOS-IT)? SILICOS-IT: Fragmental method calculated by |
-2.76 |
| Solubility | 0.258 mg/ml ; 0.00175 mol/l |
| Class? Solubility class: Log S scale |
Soluble |
| GI absorption? Gatrointestinal absorption: according to the white of the BOILED-Egg |
High |
| BBB permeant? BBB permeation: according to the yolk of the BOILED-Egg |
No |
| P-gp substrate? P-glycoprotein substrate: SVM model built on 1033 molecules (training set) |
No |
| CYP1A2 inhibitor? Cytochrome P450 1A2 inhibitor: SVM model built on 9145 molecules (training set) |
No |
| CYP2C19 inhibitor? Cytochrome P450 2C19 inhibitor: SVM model built on 9272 molecules (training set) |
No |
| CYP2C9 inhibitor? Cytochrome P450 2C9 inhibitor: SVM model built on 5940 molecules (training set) |
No |
| CYP2D6 inhibitor? Cytochrome P450 2D6 inhibitor: SVM model built on 3664 molecules (training set) |
No |
| CYP3A4 inhibitor? Cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibitor: SVM model built on 7518 molecules (training set) |
No |
| Log Kp (skin permeation)? Skin permeation: QSPR model implemented from |
-6.61 cm/s |
| Lipinski? Lipinski (Pfizer) filter: implemented from |
0.0 |
| Ghose? Ghose filter: implemented from |
None |
| Veber? Veber (GSK) filter: implemented from |
0.0 |
| Egan? Egan (Pharmacia) filter: implemented from |
0.0 |
| Muegge? Muegge (Bayer) filter: implemented from |
1.0 |
| Bioavailability Score? Abbott Bioavailability Score: Probability of F > 10% in rat |
0.55 |
| PAINS? Pan Assay Interference Structures: implemented from |
0.0 alert |
| Brenk? Structural Alert: implemented from |
1.0 alert: heavy_metal |
| Leadlikeness? Leadlikeness: implemented from |
No; 1 violation:MW<1.0 |
| Synthetic accessibility? Synthetic accessibility score: from 1 (very easy) to 10 (very difficult) |
1.34 |
* All experimental methods are cited from the reference, please refer to the original source for details. We do not guarantee the accuracy of the content in the reference.

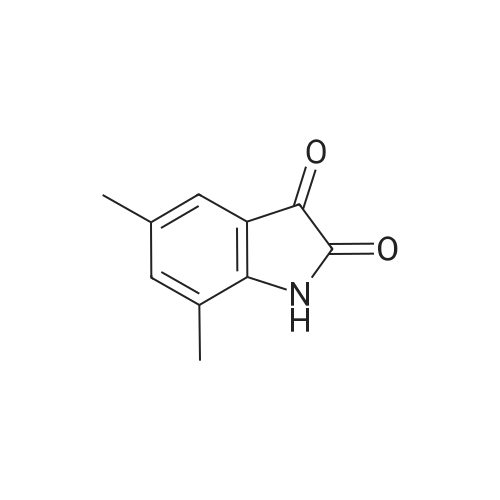
A204326[ 39603-24-2 ]
5,7-Dimethylindoline-2,3-dione
Similarity: 0.97

A204326[ 39603-24-2 ]
5,7-Dimethylindoline-2,3-dione
Similarity: 0.97

A204326[ 39603-24-2 ]
5,7-Dimethylindoline-2,3-dione
Similarity: 0.97