| 93% |
|
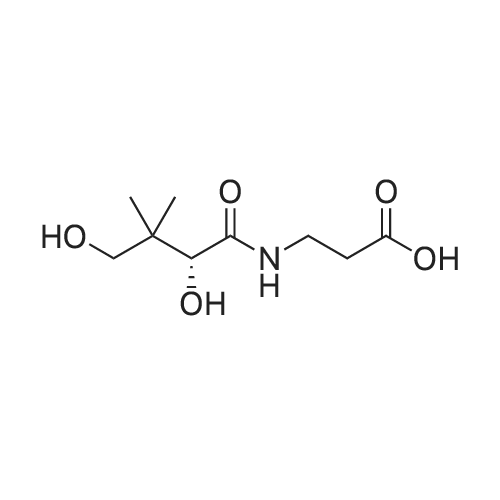
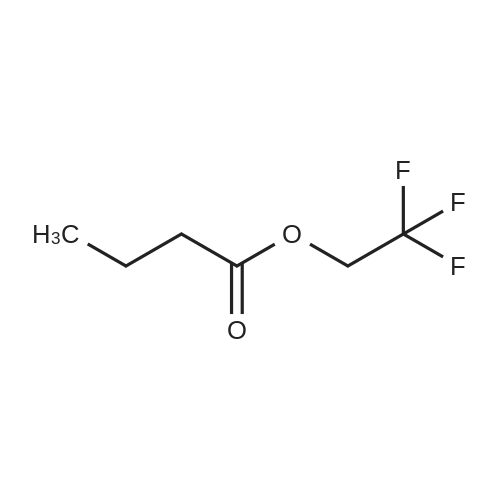
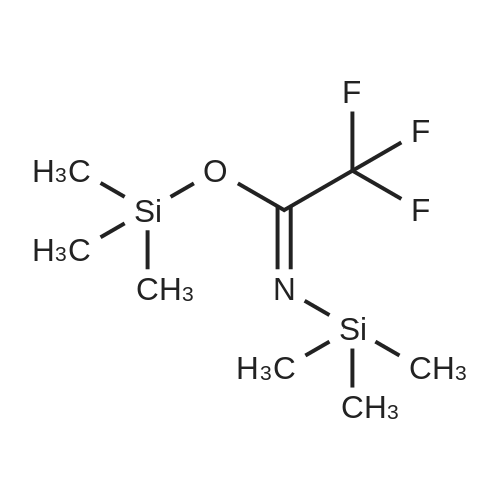
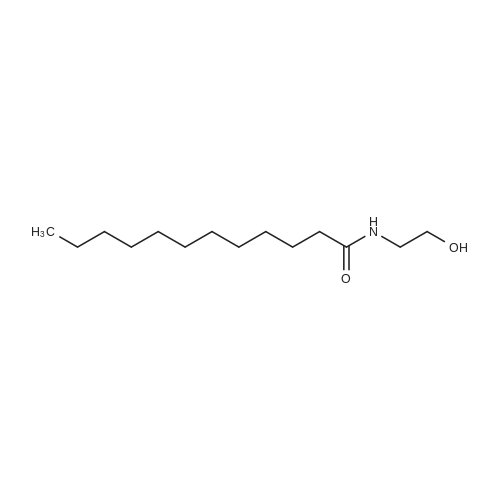
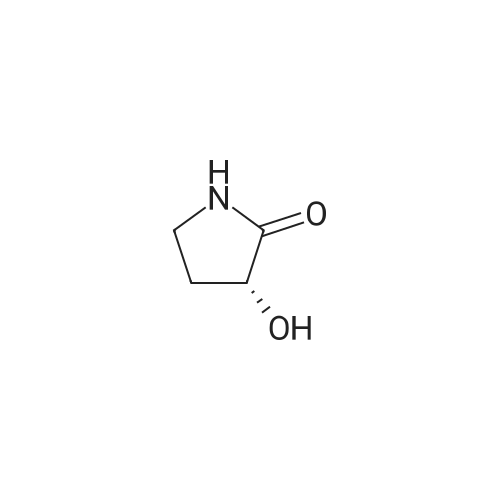
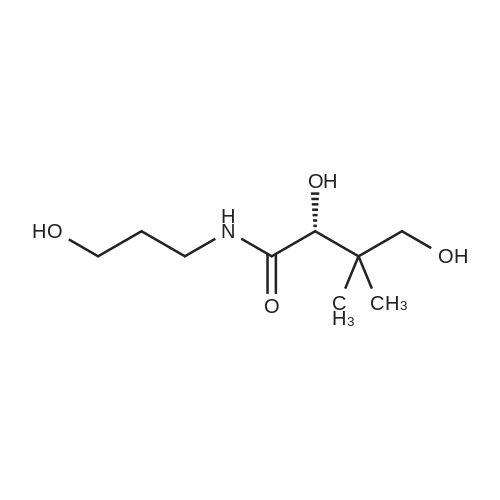
To a solution of D-Panthenol (20.5 g, 100.0 mmol, 1.0 eq.) in dry acetone (400 ml.) were added sodium sulphate anhydrous (50.0 g) and p-TsOH monohydrate (1.0 g, 4.0 mmol, 0.04 eq.). The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight. p-TsOH monohydrate (500 mg, 2.63 mmol, 0.03 eq.) was added again and the reaction mixture stirred at room temperature for 6 days until the reaction showed nearly no starting material and no further conversion anymore. Most of the acetone was removed under low pressure and the residue was suspended in a saturated aqueous solution of NaHCO3 (150 ml.) and extracted five times with ethyl acetate (200 ml_). The organic layers were combined and washed with brine (100 ml_) once. The organic layer was dried over Na2SO4, filtered and the solvent was removed under low pressure. The colourless and oily residue was dried under high-vacuum at room temperature to yield 22.7 g (93 %) of the product as a white solid. 1H NMR (CDCI3) delta = 1.01 (s 3H), 1.05 (s, 3H), 1.44 (s, 3H), 1.47 (s, 3H), 1.70-1.73 (m, 2H), 3.27-3.71 (m, 9H), 4.11 (s, 1H), 6.85 (s, 1H). 13C NMR (CDCI3) <5 = 18.7, 18.9, 22.1 , 29.4, 32.4, 33.0, 35.3, 59.1 , 71.5, 76.6, 99.1 , 171.0. |
| 59% |
With toluene-4-sulfonic acid; sodium sulfate; at 20℃; for 4.0h; |
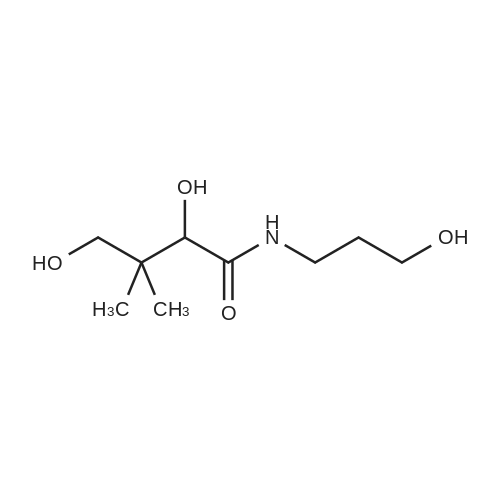
(4R)-N-(3-hydroxypropyl)-2,2,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3-dioxane-4-carboxamide (E-14) D-panthenol (10 mmol), anhydrous Na2SO4 (35.20 mmol) and PTSA monohydrate (0.99 mmol) was stirred in anhydrous acetone (40 mL) at room temperature during 4 hours. The reaction mixture was filtered and the filtrate concentrated under reduced pressure. The crude was purified by chromatography on a silica gel column (eluent: CH2Cl2/CH3OH 0 to 10%) to give the expected compound as a white crystallized solid in 59% yield. 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, 400 MHz) delta (ppm) 0.89 (s, 3H), 0.91 (s, 3H), 1.37 (s, 6H), 1.55 (quintuplet, J=6.52 Hz, 2H), 3.03-3.11 (m, 1H), 3.17-3.25 (m, 2H), 3.38-3.43 (m, 2H), 3.63 (d, J=11.48 Hz, 1H), 4.02 (s, 1H), 4.49 (t, J=5.18 Hz, 1H), 7.45-7.48 (m, 1H). |
| 54% |
|
Example 1 : Synthesis of the panthenyl docosahexaenoate of formula A1. Synthesis of intermediate compound I derived from panthenol (protection of the alcohol functional groups on the left side of panthenol)D-panthenol (CAS 81 -13-0) Compound IA 2000 ml three-neck flask, purged and maintained under a nitrogen atmosphere, is used to synthesize this compound.120 ml of trimethylchlorosilane (TMCS) was added drop wise with stirring at a temperature of 10-15 C to a solution of (2R)-2,4-dihydroxy-N- (3-hydroxypropyl)-3,3-dimethylbutanamide (D-panthenol, 100 g, 0.488 mol, 1 .00 eq) in acetone (1 I). The solution obtained was then stirred for 3 hours at room temperature, and the pH of the solution was adjusted to 7 with triethylamine. The resulting solution was then concentrated under vacuum, and the residue was applied to a silica gel column with a mixture of petroleum ether and acetone (5.5: 1 ).65 g (54%) of (4R)-N-(3-hydroxypropyl)-2,2,5,5-tetramethyl-1 ,3- dioxane-4-carboxamide (compound I) was obtained as a white solid.LC-MS of compound I: (ES, m/z):268 [M+Na]+, 513 [2M+Na]+ |

 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
 Inhibitors/Agonists
Inhibitors/Agonists
 Material Science
Material Science














 For Research Only
For Research Only
 120K+ Compounds
120K+ Compounds
 Competitive Price
Competitive Price
 1-2 Day Shipping
1-2 Day Shipping